Choosing the right type of proxy can help optimize costs and increase the success rate in various online tasks. To make the right choice, it’s essential to understand how proxies are classified and the unique characteristics of each type. In this article, VietVPS will guide you on how to differentiate among various types of proxies, providing you with a clear understanding and helping you select the most suitable option.
1. Classification by Direction
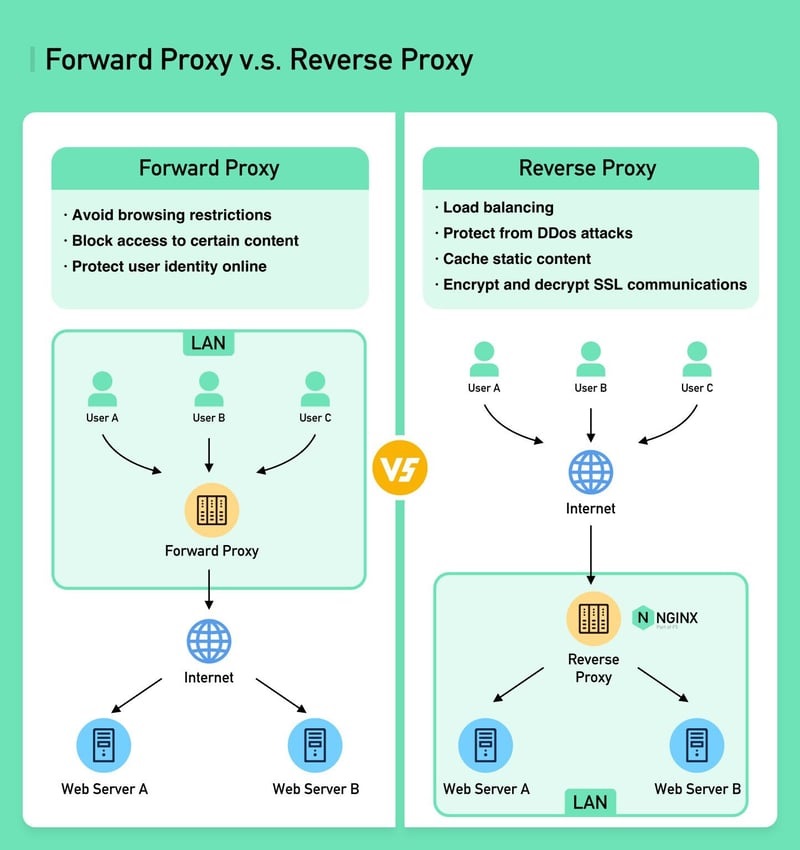
Proxies can be divided into two main types based on direction: Forward Proxy and Reverse Proxy.
-
Forward Proxy
This is the proxy that users directly interact with. Requests go from the user to the proxy server, then to the Internet, and finally connect to the backend servers of the website.
Flow Diagram: Client → Proxy → Internet → Web -
Reverse Proxy
Managed by the website, requests move from the user through the Internet to the website’s proxy server, and then to the backend servers.
Flow Diagram: Client → Internet → Proxy → Web
2. Classification by Origin
Based on origin, proxies can be categorized into four main types: Datacenter Proxy, Residential Proxy, Mobile Proxy, and ISP Proxy.
- Datacenter Proxy: Created from data centers, these proxies are easy to detect due to shared IP locations.
- Residential Proxy: Uses IP addresses from residential locations, making them harder to detect and less likely to be blacklisted.
- Mobile Proxy: A residential IP proxy using a SIM card rather than WiFi for connection flexibility.
- ISP Proxy (Static Residential): Combines Residential and Datacenter Proxies, using Internet Service Providers (ISP) instead of data centers or residential addresses.
3. Classification by Exclusivity
Proxies can also be classified based on exclusivity, dividing them into three types: Shared Proxy, Semi-Dedicated Proxy, and Dedicated Proxy.
- Shared Proxy: Also called a public proxy, it’s inexpensive but shared among multiple users, making it more susceptible to blocking and less stable.
- Semi-Dedicated Proxy: Similar to Shared Proxy but shared among fewer users (typically around three), offering improved stability.
- Dedicated Proxy (Private): A single-user proxy, providing higher speed, stability, and security for critical tasks.
4. Classification by Rotation
Based on IP rotation, proxies can be split into Rotating Proxy and Static Proxy.
- Rotating Proxy: The IP address changes with each access or after a set time, helping avoid detection.
- Static Proxy: The IP remains the same over a long period, ideal for accounts that require a stable connection.
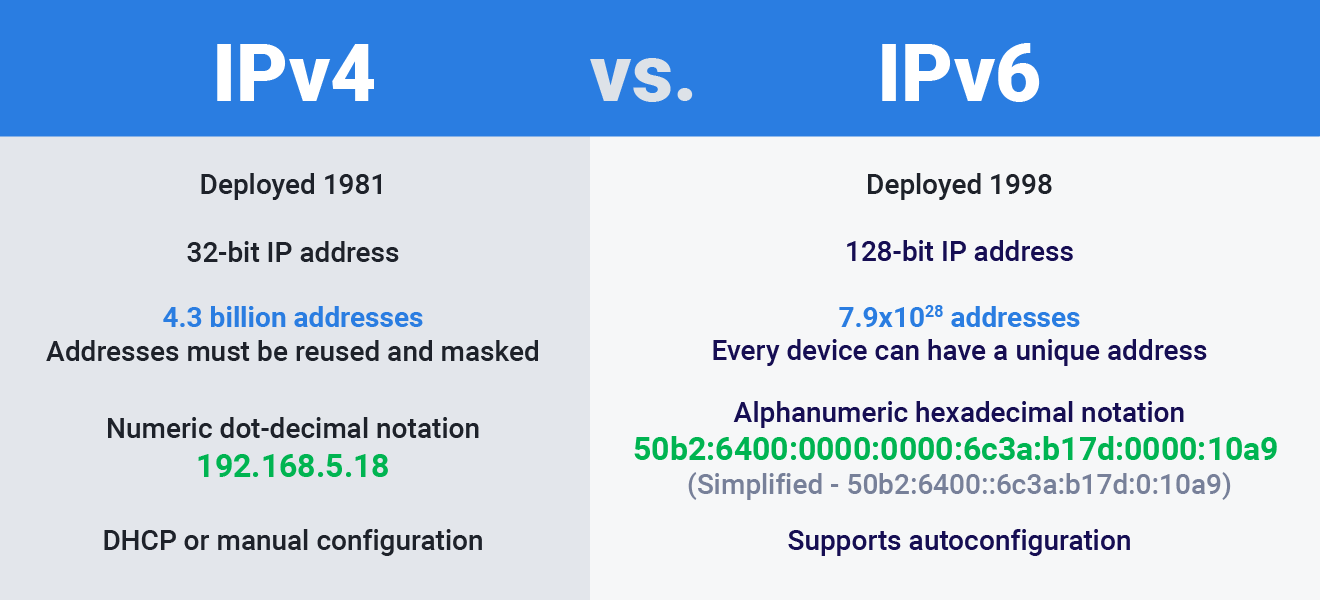
5. Classification by IP Version
Today, there are two main IP versions: IPv4 and IPv6.
- IPv4 Proxy: Widely supported by apps and websites, but limited in supply, making it challenging to find a clean IPv4 proxy.
- IPv6 Proxy: Introduced in 2012, it has more availability than IPv4, but fewer applications and websites support it.
6. Classification by Protocol
Proxies can be classified into three primary types based on protocol: HTTP Proxy, HTTPS Proxy, and Socks Proxy.
- HTTP Proxy: Accessible on HTTP and HTTPS sites, though user data is not encrypted, making it vulnerable to interception.
- HTTPS Proxy: Similar to HTTP but with encrypted data for better security.
- Socks Proxy: A more flexible option that can access any website, providing better security as it only forwards data without reading it.
7. Classification by Anonymity
Depending on the level of anonymity, proxies can be categorized into three types: Transparent Proxy, Anonymous Proxy, and High Anonymous Proxy (Elite).
- Transparent Proxy: Often used in public WiFi, this proxy does not change the user’s IP address, making it easily detectable.
- Anonymous Proxy: Masks the user’s IP, but websites can still detect the use of a proxy.
- High Anonymous Proxy (Elite): Hides the user’s IP without revealing the presence of a proxy, offering top-level privacy.
Understanding and choosing the right proxy type for your needs can greatly enhance productivity and cost-efficiency. We hope this guide has given you a comprehensive overview of the different proxy types. To optimize for personal use, consider the specific characteristics of each proxy type and select the solution that best aligns with your goals.








